I am reading a fascinating book this January (xmas gift from the parents) by Jonathan Raban called Driving Home: An American Journey. He is a wonderful writer, and in the introduction he discusses his love of reading, travel and landscapes. He puts all of these into a kind of analytical framework, and discusses how one can observe and consider writing, language, and landscapes as a way to better understand people, context, place and history. Consider this marvelous paragraph:
Trying to understand the habitat in which we live requires an ability to read it - and not just in a loose metaphorical sense. Every inhabited landscape is a palimpsest (this is me now: what an awesome word! see below for definition), its original parchment nearly blackened with the cross-hatching of successive generations of authors, claiming this place as their own and imposing their designs on it, as if their temporary interpretations would stand forever. Later overwriting has obscured all but a few, incompletely erased fragments of the earliest entries on the land, but one can still pick out a phrase here, a word there, and see how the most recently dried layer is already being partially effased with fresh ink.
From wikipedia: A palimpsest is a manuscript page from a scroll or book from which the text has been scraped off and which can be used again. I had not heard of its used as a metaphor for a landscape before, but I like it!
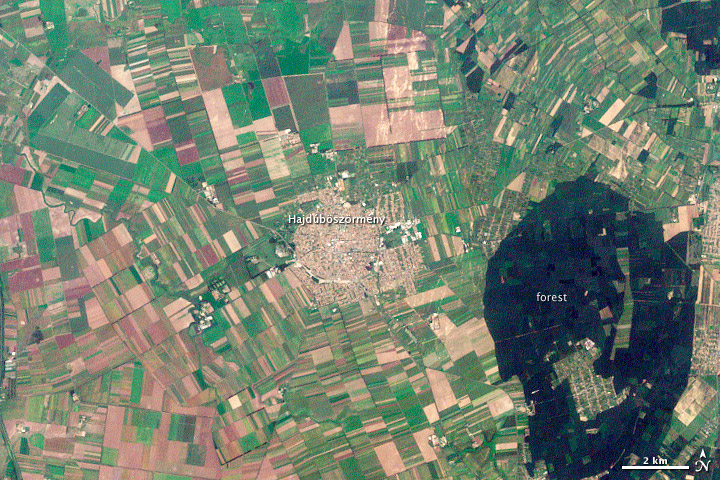 Hajdúböszörmény, Hungary. LandsatYesterday this NASA image post came across my screen as a fitting example of what Raban is talking about. In the text that accompanies the image, they say "The history of Hajdúböszörmény, Hungary, echoes across its name and over its outline on the land." They go on to discuss the derivation of its name, which echoes past conflicts and local economy, and show how its history is written on the land, in layers of land use.
Hajdúböszörmény, Hungary. LandsatYesterday this NASA image post came across my screen as a fitting example of what Raban is talking about. In the text that accompanies the image, they say "The history of Hajdúböszörmény, Hungary, echoes across its name and over its outline on the land." They go on to discuss the derivation of its name, which echoes past conflicts and local economy, and show how its history is written on the land, in layers of land use.
"The city is round, a shape easily defended on the flat North Pannonian Plain in northeastern Hungary. The livestock-based economy may also play a role in the shape of the city. The center is densely built, a concentrated ellipse of tan and white. Surrounding the center is a slightly less dense circle, marked by diagonal roads, which held stockyards and gardens. Even today, tiny spots of green indicate that this area contains more open garden space than the city center."
Hooray for geography, landscape history and remote sensing. All fascinating subjects to study. And, I recently found this blogpost from Tim DeChant, former grad student and honorary geographer, in which he describes "ghosts of geography".
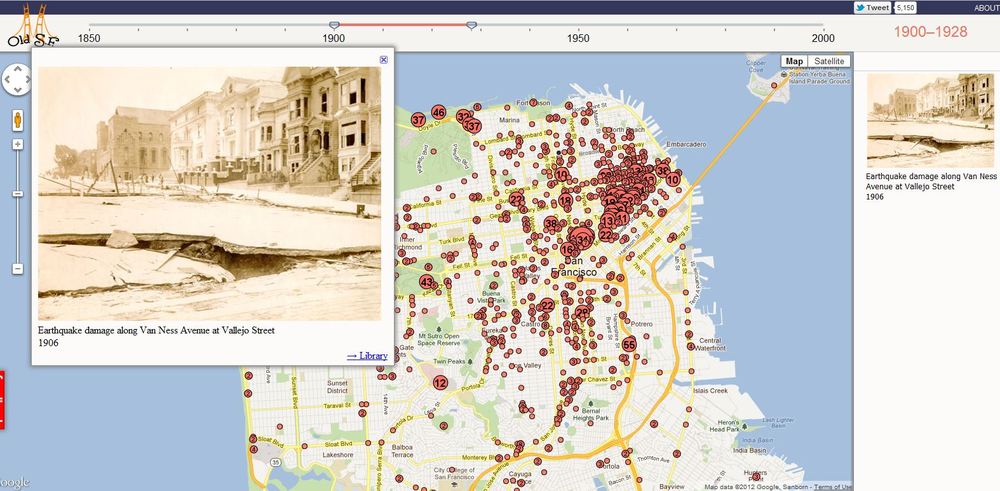







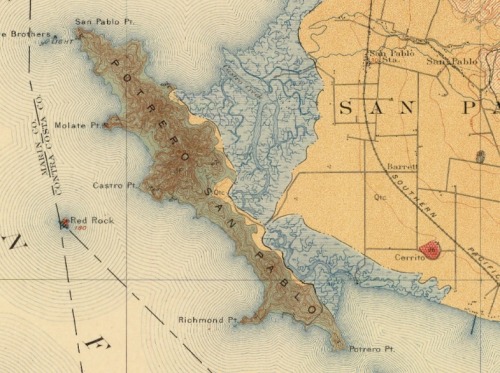
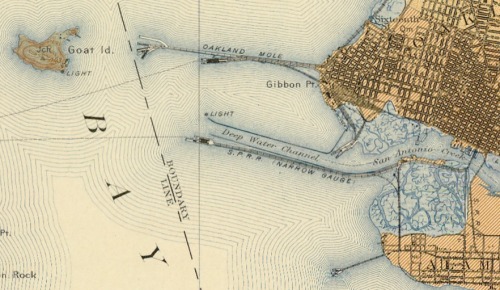
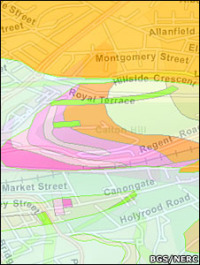



 Eric Sanderson is visiting CNR next week: Chris G pointed me to his work. Imagining Manhattan before European contact through visualization. Gorgeous work, and appealing on many levels for geographers everywhere.
Eric Sanderson is visiting CNR next week: Chris G pointed me to his work. Imagining Manhattan before European contact through visualization. Gorgeous work, and appealing on many levels for geographers everywhere. 