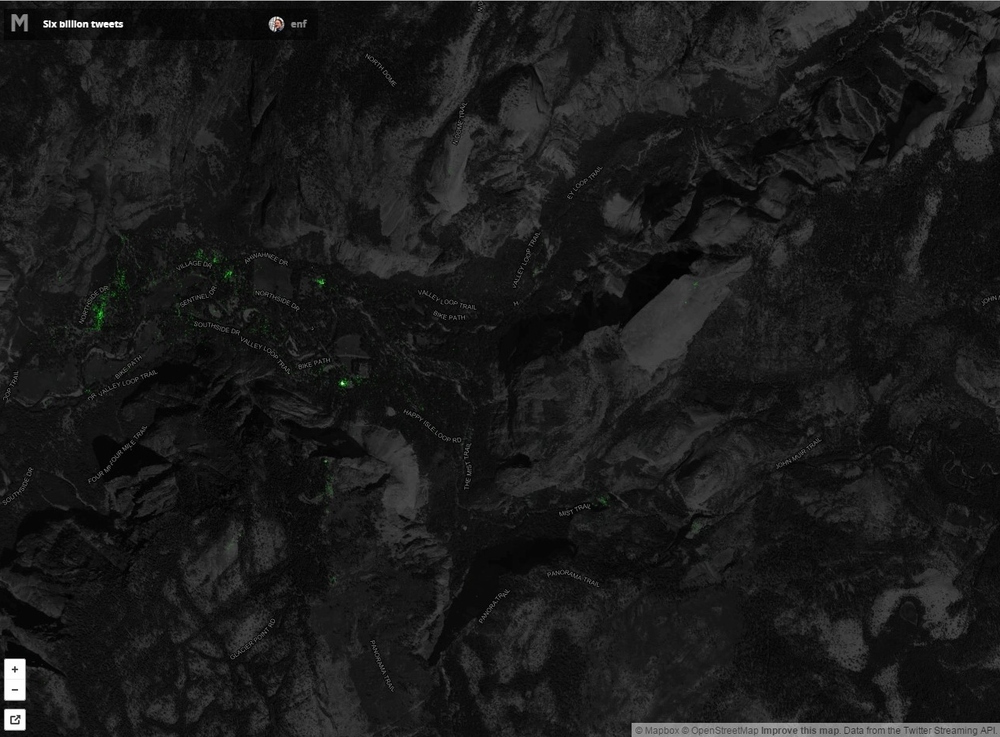
New software developed by Carnegie Mellon University in Pittsburgh and INRIA in Paris mines the geotagged imagery in Google Street View to uncover what architectural features distinguish one city from another across the globe. The software is based upon a discriminative clustering algorithm to distinguish features in one picture from another. This research shows that geographically representative image elements can be discovered automatically from Google Street View imagery in a discriminative manner.
Jacob Aron from the New Scientist reports:
"The researchers selected 12 cities from across the globe and analysed 10,000 Google Street View images from each. Their algorithm searches for visual features that appear often in one location but infrequently elsewhere...It turns out that ornate windows and balconies, along with unique blue-and-green street signs, characterise Paris, while columned doorways, Victorian windows and cast-iron railings mark London out from the rest. In the US, long staircases and bay windows mean San Francisco, and gas-powered street lamps are scattered throughout Boston."
"The discovered visual elements can also support a variety of computational geography tasks, such as mapping architectural correspondences and influences within and across cities, finding representative elements at different geo-spatial scales, and geographically-informed image retrieval."
Read the full story by clicking here.
To read the research paper and view the project website click here.