Debris from Japanese tsunami steadily drifting toward California
/This item got heavy news rotation this morning: the considerable debris from the tsunami in Japan is out to sea and slowly moving toward Hawaii and the west coast of the US.
The debris is moving east at roughly 10 miles a day, and is spread over an area about 350 miles wide and 1,300 miles long -- an area roughly the size of California. It should reach beaches and coastal cities in California, Oregon and Washington in 2013 or early 2014. These estimates are from a computer model, the details of which are spotty in the articles I read. Example here from insidebayarea.
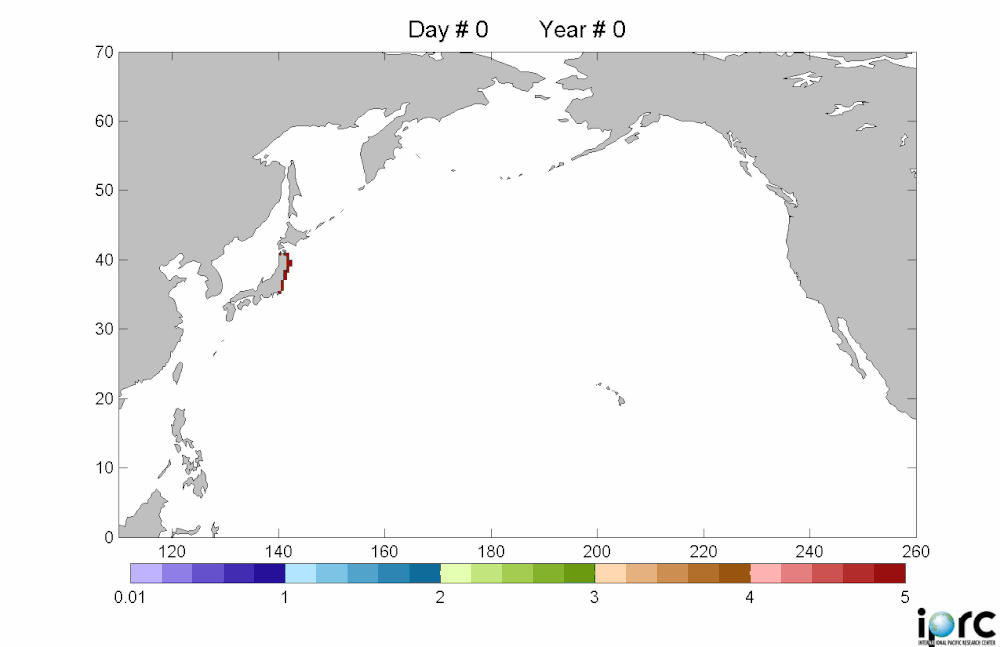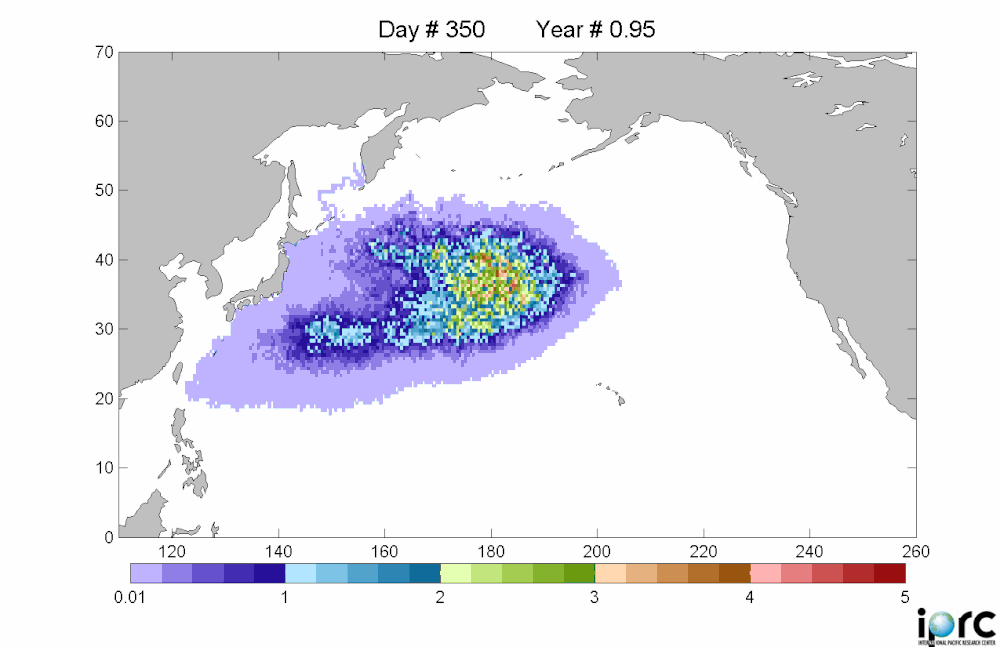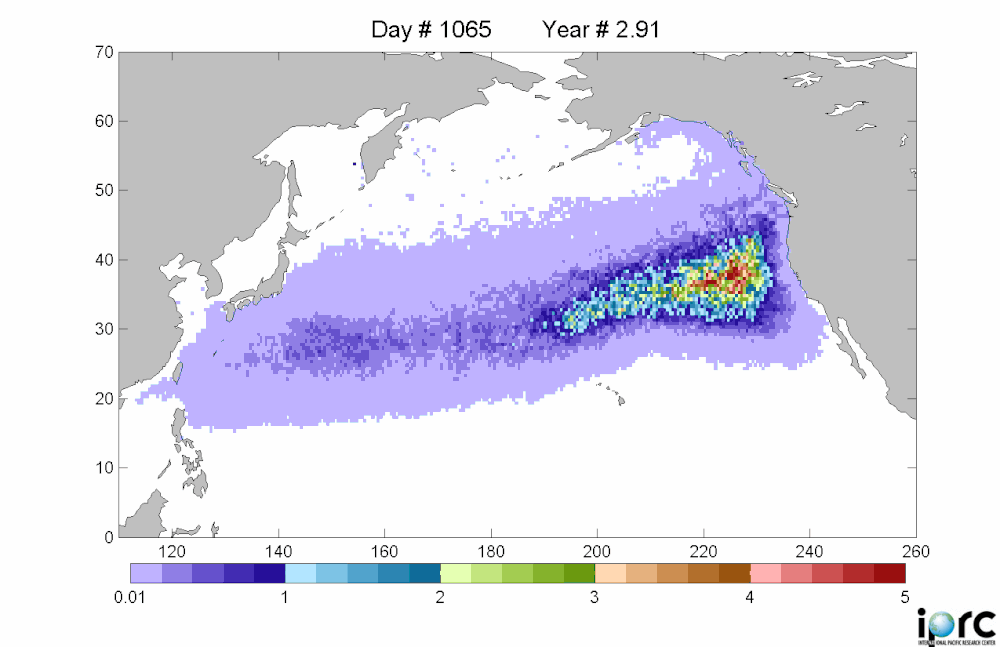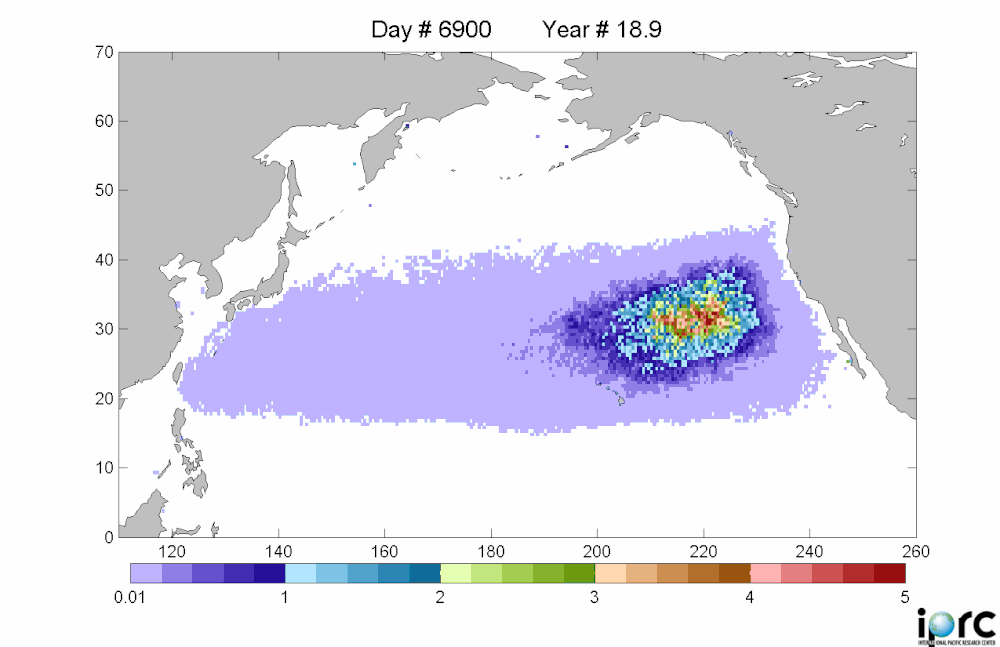 Debris movement similation: purple is low density, red is high density of debrisThere is considerable concern about this. Last Monday, representatives from the Coast Guard, NOAA, the Environmental Protection Agency, the U.S. State Department and other agencies met for the first time in Honolulu to share information about the Japanese debris and begin to chart a strategy.
Debris movement similation: purple is low density, red is high density of debrisThere is considerable concern about this. Last Monday, representatives from the Coast Guard, NOAA, the Environmental Protection Agency, the U.S. State Department and other agencies met for the first time in Honolulu to share information about the Japanese debris and begin to chart a strategy.
Among their plans: to notify the U.S. Navy and commercial shipping companies that regularly sail across the Pacific so they can begin to document what is floating. That could lead to expeditions to go map and study it.
Curtis Ebbesmeyer, a Seattle oceanographer who has studied marine debris for more than 20 years (and done some neat work with rubber duckies to map ocean currents) is one of the leads interviewed for the report.